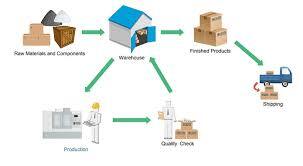
Inventory management is the backbone of any business dealing with physical goods. Effective inventory management ensures that a company has the right products in the right quantity for sale, at the right time. It also helps in minimising costs, optimising cash flow, and improving customer satisfaction. This article will explore the key aspects of the inventory management process and its importance in business operations.
Understanding Inventory Management
Inventory management involves overseeing the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to the point of sale. It is a complex process that includes various activities such as:
- Purchasing: Acquiring goods to sell or use in production.
- Storing: Safeguarding goods in warehouses until they are needed.
- Tracking: Monitoring inventory levels to ensure that stock is always available when needed.
- Reordering: Replenishing stock to avoid stockouts.
- Controlling: Ensuring the right amount of inventory is held to meet demand without incurring excess costs.
Key Components of Inventory Management
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future customer demand to ensure that the right amount of stock is available. This can be done using historical sales data, market trends, and other analytical tools.
- Inventory Control Systems: Implementing systems and technologies to monitor inventory levels, such as barcoding, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), and inventory management software. These systems help in real-time tracking and management of inventory.
- Stock Keeping Units (SKUs): Using unique identifiers for each product to keep track of inventory efficiently. SKUs help in distinguishing different products and variations.
- Order Management: Managing the process of receiving and fulfilling customer orders. This includes processing orders, picking and packing items, and shipping them to customers.
- Warehouse Management: Organizing and controlling warehouse operations to ensure efficient storage and movement of goods. This includes layout planning, inventory placement, and optimizing warehouse space.
Inventory Management Techniques
- Just-In-Time (JIT): A strategy where inventory is ordered and received only when needed. This minimizes holding costs but requires precise demand forecasting.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): A formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering and holding costs.
- ABC Analysis: Categorizing inventory into three groups (A, B, and C) based on their importance and value. ‘A’ items are high-value with low sales frequency, ‘B’ items are moderate in both value and sales frequency, and ‘C’ items are low-value with high sales frequency.
- Safety Stock: Keeping extra inventory on hand to mitigate the risk of stockouts due to unpredictable demand or supply chain disruptions.
- Dropshipping: A fulfillment method where a store doesn’t keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, it purchases the item from a third party and has it shipped directly to the customer.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
- Cost Reduction: Reducing holding costs and minimizing waste by maintaining optimal inventory levels.
- Improved Cash Flow: Ensuring that capital is not tied up in excess inventory, thereby improving cash flow and liquidity.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Meeting customer demand promptly by having the right products in stock, which leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations by automating inventory tracking and management, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Better Decision Making: Providing accurate and real-time data on inventory levels, helping businesses make informed decisions about purchasing, sales, and production.
Challenges in Inventory Management
- Demand Variability: Fluctuating customer demand can make it challenging to maintain optimal inventory levels.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Delays and disruptions in the supply chain can lead to stockouts or excess inventory.
- Inventory Accuracy: Ensuring accurate inventory records is crucial for effective management but can be difficult to maintain.
- Cost Control: Balancing the costs associated with purchasing, holding, and managing inventory can be challenging.
- Technology Integration: Implementing and integrating advanced inventory management systems can be costly and require significant changes in operations.
Conclusion
Effective inventory management is crucial for the success of any business dealing with physical goods. It involves a combination of strategies, technologies, and best practices to ensure that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantity. By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can reduce costs, improve cash flow, enhance customer satisfaction, and increase operational efficiency. Despite the challenges, the benefits of effective inventory management make it a critical component of modern business operations.
Understanding and implementing the right inventory management techniques can lead to significant improvements in a company’s performance and profitability. By staying informed about industry trends and adopting the latest technologies, businesses can navigate the complexities of inventory management and achieve long-term success.